Curved vs. Flat TVs: How Screen Shape Changes Everything

A decade ago, the tech industry bet big on the idea that the future of television was bent. Curved TVs arrived with massive marketing campaigns promising an IMAX-quality experience at home, only to slowly vanish from major retail shelves.
Yet the concept still generates curiosity for dedicated home theater enthusiasts and bargain hunters. The distinction is straightforward.
Flat panels provide the reliable and uniform plane we expect, while curved models attempt to match the natural arc of the human eye to enhance depth. But does that theoretical advantage actually translate to better movie nights?
Visual Immersion and Depth Perception
Manufacturers originally pitched the curved screen as a way to replicate the immersive feeling of a commercial movie theater within the home. The design philosophy centers on the idea that the shape of the display should mimic the natural mechanics of human vision.
By bending the edges of the panel toward the viewer, the technology attempts to create a more encompassing visual experience that a standard flat panel cannot quite duplicate.
The Theoretical Advantage
The primary argument for the curved design rests on the concept of equidistant viewing. When you sit in front of a large flat screen, the center of the image is closer to your eyes than the edges are.
This difference forces your eyes to adjust focus slightly as they scan from the middle to the corners, which can contribute to subtle fatigue over long periods. A curved screen maintains a more consistent distance between the viewer's eyes and every point on the panel.
This uniformity theoretically reduces optical distortion and enhances the field of view. The result is a slight improvement in depth perception, creating a mild three-dimensional effect where the image feels like it wraps around you rather than sitting on a distant plane.
The Sweet Spot Requirement
To realize these benefits, the viewer must sit in a precise location. This focal point is often referred to as the sweet spot.
If you sit too far back or too far to the side, the immersive effect collapses. The curvature dictates exactly where the optimal viewing position is, which restricts the flexibility of your furniture layout.
Screen size also plays a massive role here. The curve is barely noticeable on displays smaller than 65 inches unless you sit extremely close, which is why the technology found a second life in desktop gaming monitors.
For a living room television, a massive screen is necessary to fill enough peripheral vision to justify the bend.
Perceived Size and Scale
Another interesting optical illusion created by the curve is an increase in perceived size. Because the edges of the screen bend toward the viewer, they occupy a larger portion of the peripheral vision compared to a flat screen of identical width.
This wrapping effect tricks the brain into perceiving the image as wider and more expansive than it actually is. It creates a sense of grandeur that flat panels sometimes lack, making 75-inch or larger curved models feel particularly imposing and cinematic.
Viewing Angles and Social Functionality
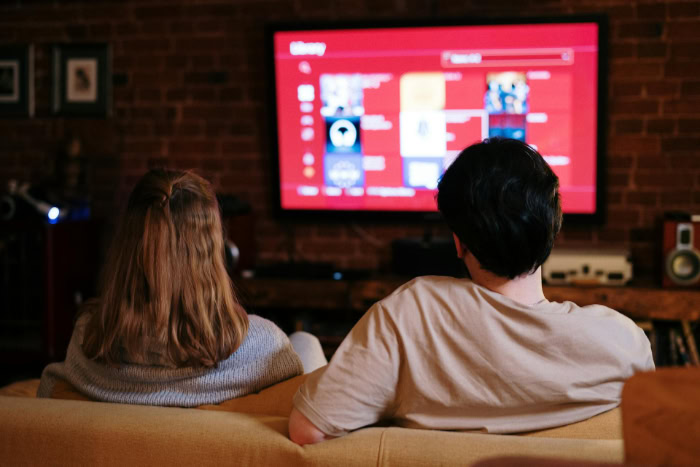

While the curve offers specific advantages for a solitary viewer, the dynamics change completely when more people enter the room. The shape of the television dictates how light is projected outward, which directly impacts how the picture looks from different positions on the couch.
Choosing between flat and curved often comes down to how many people typically watch the TV at the same time.
Solo Versus Group Viewing
Flat televisions remain the standard for living rooms because they offer a democratic viewing experience. The image quality remains relatively consistent for everyone, regardless of where they sit on a wide sofa or sectional.
Curved televisions are inherently designed for a single user in the “Captain's Chair” position. The person sitting dead center gets the perfect immersive experience, but anyone sitting off to the side gets a compromised view.
The curve that wraps around the central viewer effectively turns away from the person sitting on the end of the couch, making it a poor choice for large families or Super Bowl parties.
Off-Axis Distortion and Geometric Issues
When you view a curved screen from the side, the geometry of the image begins to warp. The side of the screen closest to you looks larger, while the far side looks smaller and compressed.
This creates a “trapezoidal effect” where rectangular objects, like a ticker at the bottom of a news broadcast or a letterbox bar, appear slanted or bowed. Furthermore, if the viewing angle is severe enough, the bezel on the near side of the TV can visually obstruct the image on the far side.
This creates a blind spot that simply does not exist on a flat panel.
Color and Contrast Consistency
Panel technology, such as LED or OLED, already suffers from some degree of color washout when viewed from an angle. A curved screen can exacerbate this issue for off-center viewers.
Because the far side of the curve angles away from a side viewer, that portion of the screen is viewed at a much steeper angle than the rest of the display. This leads to a noticeable shift in contrast and color saturation on just one half of the screen, creating an unbalanced and distracting picture for anyone not sitting in the center.
Reflections, Glare, and Room Lighting

The physical shape of a television screen drastically alters how it interacts with ambient light in a room. Lamps, overhead fixtures, and windows create reflections that can ruin the viewing experience.
While no glossy screen is immune to glare, the difference in how flat and curved surfaces manipulate these reflections is significant and often frustrating for owners of curved displays.
Physics of Light Interaction
A flat screen acts like a standard mirror. If a lamp is reflected in the screen, you see a discrete, localized reflection of that lamp.
It is usually easy to ignore or block by closing a curtain. A curved screen functions like a concave mirror.
Instead of reflecting a single point of light, the curvature catches the reflection and stretches it across a large portion of the screen. This is frequently described as a “funhouse mirror” effect.
A small light source that would be a minor annoyance on a flat TV becomes a long, distorted streak of glare on a curved one, obscuring a much larger section of the movie or game.
Managing Glare and Ambient Light
There are specific scenarios where the curve actually helps with light management. If a light source is positioned at a specific angle to the side, the curve of the screen might shield the panel from catching it, acting like a blinder.
However, in a typical bright living room with multiple windows or open-concept lighting, the curve tends to be a disadvantage. The concave shape captures light from a wider range of angles than a flat plane does.
It collects reflections from around the room and focuses them toward the viewer, making it much harder to control glare without completely darkening the environment.
Aesthetics, Design, and Installation
The physical shape of a television dictates how it integrates into a living space. While picture quality is the primary performance metric, the design of the chassis determines how the unit looks when it is turned off.
Modern interior design favors clean lines and unobtrusive technology, which creates a distinct conflict between the architectural simplicity of flat panels and the aggressive profile of curved displays.
Wall Mounting Challenges
Mounting a television is the preferred method for many homeowners seeking a streamlined look. Flat panels excel here. They are engineered to sit flush against the wall, often protruding less than an inch.
High-end “gallery” designs essentially disappear into the room, mimicking the appearance of a framed photograph or painting. Curved televisions struggle significantly in this area.
Because the edges bow outward, the center of the TV touches the mount while the sides curl away from the wall. This leaves a large, visible gap that breaks the illusion of a floating screen.
It casts odd shadows behind the unit and exposes the cabling and mounting hardware that a flat screen would normally hide.
Stand-Mounted Aesthetics
The narrative changes when the television sits on a media console or entertainment unit. A curved TV on a stand often looks like a piece of modern sculpture.
The arc creates a self-supporting structure that feels futuristic and tech-forward. For a room where the TV is meant to be the centerpiece rather than a hidden element, the curve offers a distinct visual flair.
It draws the eye immediately. This design choice signals that the device is a piece of specialized equipment, distinct from the standard black rectangles found in most homes.
Structural Integrity and Thickness
Achieving a permanent bend in a display panel requires rigid structural reinforcement. Consequently, curved televisions are almost always thicker and bulkier than their flat counterparts.
Manufacturers must use heavier housing to prevent the screen from flexing back to a straight position or warping over time. Flat panels, particularly OLED models, have achieved paper-thin profiles because they do not fight against tension.
If the goal is a sleek, minimalist profile that consumes as little space as possible, the flat panel is physically superior. The curved model demands more depth on the shelf and feels far more substantial in terms of weight and build.
Market Status: The TV vs. Monitor Divide
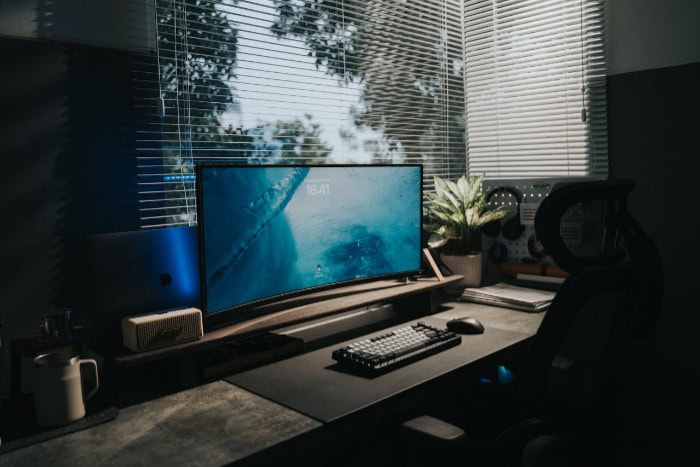

The trajectory of the curved display is a tale of two very different markets. While the technology failed to become the new standard for living room televisions, it found a devoted following in the world of high-performance desktop computing.
This divergence highlights how distance and use case determine the value of the curve.
The Decline in the Living Room
Between 2013 and 2015, major manufacturers like Samsung, LG, and Sony poured resources into curved TVs. By 2018, nearly all of them had quietly removed these models from their premium lineups.
The general consumer rejected the curve for standard home use. The drawbacks regarding viewing angles, wall mounting, and glare simply outweighed the subtle immersion benefits.
Shoppers voted with their wallets for bezel-less, ultra-thin flat wallpapers that blended seamlessly into their homes. Today, finding a brand-new curved television from a top-tier brand is nearly impossible, as the industry has collectively agreed that the flat plane is the optimal form factor for communal entertainment.
The Renaissance in Gaming
Conversely, the curve has thrived in the PC gaming sector. The logic here is sound.
A desktop user sits at a desk, roughly two to three feet from the screen, effectively occupying the perfect “sweet spot” at all times. In this controlled environment, the curve functions exactly as intended.
It brings the edges of an ultrawide monitor into the player's peripheral vision, reducing eye strain and increasing immersion during long gaming sessions. Because a monitor is a personal device rather than a social one, the poor viewing angles are irrelevant.
This success proves that the technology was not flawed, but rather misapplied to the living room television.
Buying Advice
For the average buyer looking for a main household television, the flat panel is the only logical choice. It offers the best versatility, mounting options, and social viewing experience.
The only way to acquire a curved TV today is to scour the used market. This path requires caution.
These units are now aging, and early generation curved panels often suffered from uniformity issues where the backlight would bleed through the stress points of the curve. Unless you are building a specialized, single-seat home theater or a retro-tech setup, a modern flat 4K or 8K display provides superior performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Choosing between a curved and a flat display comes down to a fundamental trade-off between singular immersion and practical versatility. The curve offers a genuine optical advantage by wrapping the image around the viewer, but this benefit is locked behind a strict requirement to sit in the exact center of the screen.
While the immersive “sweet spot” creates a compelling sense of depth, it comes at the cost of distorted viewing angles for guests, complicated wall mounting, and distracting reflections. For the overwhelming majority of home theater setups and family living rooms, the flat television remains the superior choice.
It offers a consistent experience for multiple viewers and integrates seamlessly into modern home decor. The curved screen has found its true home on the desktop, where high-performance gaming monitors utilize the bend to great effect for a single user.
Unless you are equipping a dedicated PC battle station, stick to the flat panel for a reliable and distortion-free viewing experience.


