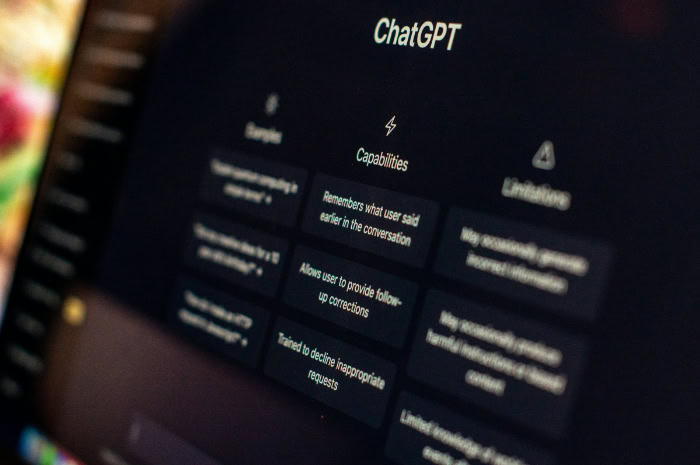
How Does ChatGPT Work? What You Need to Know

ChatGPT produces text that feels startlingly human. The responses arrive with such speed and coherence that interacting with the software often resembles a conversation with a thinking being.
Yet there is no mind behind the cursor. The “magic” users experience is actually a complex layer of statistics and probability.
ChatGPT is a Large Language Model powered by machine learning. It functions as a sophisticated prediction engine rather than a conscious entity.
The Foundation: What Is “GPT”?
The name ChatGPT serves as more than just a brand label. It acts as a technical blueprint that describes exactly how the software operates.
To grasp what this technology does, one must look at the specific engineering concepts hidden within the acronym itself. These components explain how a machine can process human language and generate coherent responses without possessing a mind of its own.
Decoding The Acronym
The name breaks down into three distinct concepts that define the model's architecture.
Generative: This refers to the AI's ability to create entirely new strings of text. Unlike a search engine that finds and displays existing web pages, this model calculates and constructs sentences word by word. It does not copy and paste answers from a database. It generates unique responses every time based on the input it receives.
Pre-trained: This indicates that the learning process happened before the public ever gained access to the tool. The model arrives with a massive, fixed repository of information already processed. It does not learn new facts from users in real-time during a standard conversation. All its “knowledge” comes from the massive training run it completed previously.
Transformer: This is the specific type of neural network architecture that makes modern AI possible. The Transformer mechanism allows the model to track relationships between words across long distances in a text. For example, if a sentence mentions “John” at the start and then uses the word “he” a paragraph later, the Transformer architecture links “he” back to “John.” This capability allows the AI to maintain context over long conversations rather than treating every sentence as an isolated event.
The Large Language Model (LLM)
ChatGPT belongs to a class of technology known as Large Language Models. An LLM is a complex algorithm designed to interpret, summarize, and predict text.
These models run on massive datasets containing billions of words. By analyzing this data, the algorithm learns to predict the next plausible word in a sequence. It functions as a probability engine that assigns mathematical values to language.
Phase One: Pre-Training (Reading The Internet)
The first phase of creating ChatGPT involves exposing the model to an immense amount of text. Engineers feed the system a diet of information that encompasses a significant portion of the public internet.
This process is computationally expensive and can take months to complete. The goal is to create a broad foundation of general knowledge and linguistic ability.
Ingesting The Data
The training corpus consists of a diverse range of text sources. The model consumes thousands of books, countless articles, academic papers, websites, and lines of computer code.
This variety ensures the AI is exposed to different writing styles, from formal academic prose to casual internet slang. It also allows the model to learn various coding languages and technical formats.
Pattern Recognition
During this phase, the model does not memorize facts in the way a human memorizes a phone number. Instead, it analyzes the statistical structure of language.
It maps how words relate to one another. The system learns grammar rules, syntax, and the associations between concepts by observing how often words appear together.
It builds a mathematical map of language where “doctor” is closely linked to “hospital” and “medicine.”
Unsupervised Learning
The learning process is largely unsupervised. This means the model trains without explicit human guidance or correction during this stage.
It continuously attempts to predict the next word in a sentence. When it guesses correctly, its internal connections are strengthened.
When it guesses incorrectly, it adjusts its parameters to improve future predictions. This cycle repeats billions of times until the model becomes highly proficient at anticipating how sentences should end.
The Resulting “Base Model”
At the end of pre-training, the result is a “base model.” This version of the AI is incredibly powerful but often unpredictable.
It can generate coherent text and solve problems, yet it lacks direction. If a user asks a base model a question, it might answer it, or it might simply generate more questions similar to the first one.
It is prone to rambling or generating nonsensical outputs because it has not yet learned how to interact helpfully with a human user.
Phase Two: Fine-Tuning And Human Feedback
A base model knows how to speak, but it does not know how to be a helpful assistant. To fix this, developers move to the fine-tuning phase.
This stage shifts the focus from quantity of data to quality of interaction. Through rigorous training and human evaluation, the raw prediction engine is refined into a tool that follows instructions and adheres to safety standards.
Instruction Tuning
The first step in refinement is instruction tuning. Developers train the model on a specialized dataset of questions and answers.
This teaches the AI that when it receives a prompt, it should provide a response rather than just continuing the text. This process aligns the model with the user's intent.
It transforms the AI from a simple text completor into a conversational partner that attempts to satisfy specific requests.
Reinforcement Learning From Human Feedback (RLHF)
This is a critical step where human involvement directly shapes the AI's behavior. Humans review multiple responses generated by the model for a single prompt.
They rank these responses from best to worst based on quality, accuracy, and tone. The AI analyzes this data to build a “reward model.”
This internal scoring system helps the AI predict which answers humans will prefer in the future. It encourages the model to be helpful and harmless while discouraging responses that are vague or rude.
Safety Layers
Throughout the fine-tuning process, engineers implement safety protocols. These guardrails are designed to prevent the model from fulfilling harmful requests.
If a user asks for instructions on how to commit a crime or generate hate speech, the model is trained to refuse. These layers act as a filter.
They ensure the powerful capabilities of the base model are constrained within ethical and legal boundaries before the tool is released to the public.
The Execution: How It Generates Answers

When a user types a prompt into ChatGPT, the response appears almost instantly. This speed hides a complex sequence of mathematical operations occurring behind the scenes.
The model does not simply look up an answer in a library or database. It constructs the reply from scratch, piece by piece, relying on the probability patterns it learned during its massive training phase.
Tokenization
The AI does not read sentences the way humans do. It breaks text down into smaller chunks called tokens.
A token can be a whole word, part of a word, or even a single character. For example, the word “planning” might be split into “plan” and “ning.”
The model converts these chunks into numerical values. This conversion allows the neural network to process the text as a sequence of numbers rather than a string of letters, effectively translating human language into a format the machine can calculate.
Next-Token Prediction
Once the input is tokenized, the core engine begins its work. The model analyzes the sequence of numbers and calculates which token is most likely to come next.
It looks at the probability of every possible following word based on the patterns it observed during training. If the sentence starts with “The sun rises in the,” the model assigns a very high probability to the word “east” and a statistically insignificant probability to words like “west” or “sandwich.”
It repeats this prediction process for every single word it generates.
The Element Of Randomness
If the model always picked the single most likely word, its writing would become repetitive and robotic. To prevent this, engineers introduce a parameter often called “temperature.”
This feature adds a calculated degree of randomness to the selection process. Instead of always choosing the top prediction, the AI might select a slightly less probable word.
This variation creates text that feels more creative and human. It ensures that asking the same question twice might yield slightly different phrasing each time.
The Context Window
One of the most useful features of the system is its short-term memory, known as the context window. This mechanism allows the AI to reference previous parts of the conversation.
When generating a new answer, it processes the recent exchange to ensure continuity. This is why a user can say “Change that to blue,” and the model correctly identifies what “that” refers to based on the prior interaction.
However, this window has a limit; if a conversation goes on too long, the model will eventually lose track of the beginning.
The Limitations: What It Cannot Do
Despite its impressive fluency, ChatGPT operates with significant constraints. It is a tool built on statistics rather than a repository of verified truth.
Recognizing where the technology fails is just as important as recognizing its capabilities. These limitations define the boundary between artificial text generation and actual human intelligence.
Probabilistic Versus Factual
The model is designed to create plausible text, not to verify facts. Its primary goal is to predict the next word in a sequence that sounds grammatically and contextually correct.
Consequently, it prioritizes flow and coherence over accuracy. It can generate a completely false sentence that looks perfect because the words fit together statistically, even if they do not reflect reality.
The model has no concept of truth; it only has a concept of likelihood.
Hallucinations
This reliance on probability leads to a phenomenon known as hallucination. This occurs when the AI confidently states a falsehood as a fact.
The model might invent a court case that never happened or attribute a quote to the wrong person. Because the AI speaks with an authoritative and professional tone, these errors can be difficult to spot.
The machine does not know it is lying. It is simply completing a pattern that looks correct to its algorithm.
Lack Of Sentience
It is easy to project human qualities onto the software, but the model has no internal life. It does not think, feel, or experience the world.
It does not truly grasp the concepts it writes about. When it uses words like “sad” or “happy,” it is merely manipulating symbols based on math.
There is no consciousness behind the screen, only a complex set of calculations processing numbers.
Static Knowledge Base
The model's core knowledge is frozen in time. Its internal database consists only of the information provided during its training period.
Unless it is connected to external tools that can browse the live web, it remains unaware of current events. It cannot know about a news story that broke this morning or a sports score from last night because that data does not exist within its pre-trained memory.
Conclusion
ChatGPT represents a triumph of engineering rather than a spark of consciousness. It functions as a sophisticated prediction engine refined by human feedback to mimic conversation.
The system does not possess thoughts or intent; it operates strictly on probability and pattern matching. Recognizing this reality empowers the user.
When one grasps that the AI is merely completing a sequence of text based on math, it becomes easier to craft precise prompts and critically evaluate the results for accuracy.
This technology signals a fundamental shift in how we interact with data. We are no longer limited to searching for existing documents on a server.
We are now generating new information on command. This capability changes the role of the user from a passive consumer of search results to an active editor of synthetic text.
Success with these tools depends on knowing exactly how the machine thinks, or more accurately, how it computes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does ChatGPT actually comprehend what I say?
No, the software does not possess consciousness or genuine comprehension. It uses complex statistics to predict which words should follow your input based on its training data. It mimics intelligence by processing patterns and associations, but it has no thoughts, feelings, or awareness of the conversation.
Where does ChatGPT get its information?
The model was trained on a massive dataset comprising books, articles, websites, and code from the internet. It does not access a live database of facts to answer questions in the standard mode. It generates responses based on the linguistic patterns it learned during that initial training process.
Why does ChatGPT sometimes give wrong answers?
The AI prioritizes creating sentences that flow well grammatically over stating facts. This phenomenon is called hallucination. Since the model predicts words based on probability rather than verifying truth, it can confidently present false information if the sentence structure looks statistically correct to the algorithm.
Does ChatGPT learn from our conversations in real-time?
The core model does not update its permanent knowledge base from your chats. It uses a temporary short-term memory called a context window to track the current discussion. Once the conversation ends or the window fills up, that specific context is discarded from its immediate processing.
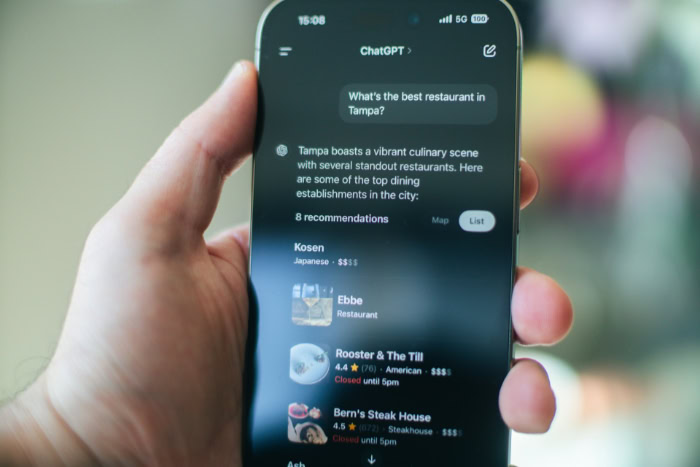
Is ChatGPT the same thing as a search engine?
No. A search engine indexes existing web pages to retrieve specific sources of information. ChatGPT generates new text word by word based on learned patterns. While search engines find data, this tool constructs answers from scratch, which makes it creative but often less reliable for sourcing specific facts.

