What Is ChatGPT and How Does It Work?
ChatGPT seemed to materialize out of thin air and immediately dominate headlines and dinner table debates alike. It went from a quiet research experiment to a household name faster than any application in history.
In simple terms, ChatGPT is an artificial intelligence chatbot designed to analyze user input and generate text that feels authentically human. It does not merely search for existing results; it predicts and constructs new answers conversationally.
Yet using it effectively requires looking past the buzz to see the machinery underneath.
Origins And Identity
ChatGPT did not appear in a vacuum; it is the product of specific research goals and corporate partnerships. Recognizing who built the system and what its name actually represents helps clarify why it behaves the way it does.
The technology sits at the intersection of academic research and commercial software, resulting in a tool that feels familiar yet operates on entirely new principles.
The Creator
The research organization responsible for ChatGPT is OpenAI. Founded initially as a non-profit artificial intelligence research lab, OpenAI later transitioned to a “capped-profit” model to attract the funding necessary for massive computing power.
While they operate independently, they have formed a significant partnership with Microsoft. This collaboration allows OpenAI to utilize Microsoft’s vast Azure cloud computing infrastructure to train its models, while Microsoft integrates OpenAI’s technology into products like Bing and Office.
The Name Decoded
The acronym “GPT” sounds technical because it describes the specific architecture of the software. It stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer.
Breaking these three words down clarifies the function of the tool. “Generative” means the model creates new data rather than retrieving existing files; it constructs answers word by word.
“Pre-trained” indicates that the model has already reviewed a massive dataset of text before you ever type a prompt, learning patterns and structures in advance. “Transformer” refers to the specific type of neural network architecture that allows the AI to track relationships between words in a sentence, giving it the ability to maintain context over long passages.
The Interface
New users often confuse ChatGPT with a standard search engine, but the user experience is distinct. The interface resembles a messaging application or a text conversation with a friend.
Instead of typing a query and receiving a list of blue links to websites, users type a prompt and receive a direct, conversational response. The design encourages back-and-forth dialogue, allowing users to ask follow-up questions, request changes to the tone, or refine the output without starting over.
How ChatGPT Works

The conversational ability of the chatbot is an illusion created by advanced mathematics and statistical probability. Beneath the simple chat window lies a complex system designed to mimic human language patterns.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
ChatGPT is the interface for a technology known as a Large Language Model (LLM). An LLM acts as the “brain” processing your inputs.
These models are neural networks containing billions of parameters, which you can think of as adjustable knobs that the model tunes during its training process. The model processes input text, analyzes the mathematical relationships between the words, and generates an output that fits the established patterns it has learned.
Prediction vs. Thinking
A common misconception is that the AI “thinks” about your question or “knows” the answer. In reality, the model performs a complex prediction task.
It calculates the statistical probability of which word (or token) should come next in a sequence based on the words that came before it. If you type “The cat sat on the,” the model predicts “mat” not because it visualizes a cat, but because “mat” is statistically the most likely next word in that context.
It creates coherent sentences through probability, not sentience or actual comprehension.
Training Data
To make these predictions accurate, the model was fed a massive corpus of text data. This dataset includes books, websites, academic articles, and computer code.
By processing this information, the model learned the structure of language, grammar rules, factual associations, and reasoning patterns. It does not store this data like a database; instead, it stores the weights and patterns derived from the data.
This explains why it can write a poem in the style of Shakespeare but might struggle to quote a specific news article from yesterday perfectly.
Reinforcement Learning
Raw language models can be unpredictable or toxic, so OpenAI uses a process called Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF). Human testers review the model's responses and rank them based on quality, safety, and helpfulness.
This feedback loop trains the model to favor answers that are useful and polite while avoiding harmful content. It aligns the raw predictive power of the LLM with human values and safety standards.
Common Use Cases

Because the model predicts language patterns rather than performing a single specific task, it serves as a general-purpose utility. Users across various industries have adapted the tool to function as a writer, a tutor, a coder, and an organizer.
The versatility of the system allows it to handle tasks ranging from the creative to the highly analytical.
Content Creation And Editing
One of the most frequent uses for ChatGPT is drafting and refining text. Users employ it to overcome writer's block by asking for outlines, article introductions, or creative titles.
It serves as an efficient editor that can rewrite clumsy sentences, check for grammatical errors, or adjust the tone of an email to sound more professional. Marketing professionals use it to generate ad copy and social media captions, while job seekers use it to tailor cover letters to specific job descriptions.
Information Synthesis And Learning
The tool functions effectively as a summarization engine. Users can paste long articles, meeting transcripts, or technical PDFs into the chat and ask for a bulleted summary of the main points.
It also acts as an on-demand tutor. A user struggling with a difficult concept can ask the AI to “explain this topic as if I am five years old,” and the model will strip away jargon to provide a simple analogy. This makes it a powerful aid for rapid learning and research.
Technical Assistance
Programmers and data analysts utilize ChatGPT to speed up their workflows. The model can write boilerplate code in languages like Python, JavaScript, and C++, saving developers time on repetitive tasks.
It can also analyze existing code to identify bugs or suggest optimizations. Beyond coding, it can solve mathematical equations and help format data, such as converting a messy list of text into a clean table or a CSV file.
Personal Productivity
Outside of professional work, the tool assists with daily logistics. It can generate weekly meal plans based on dietary restrictions and available ingredients.
Travelers use it to create day-by-day itineraries for vacations, complete with museum hours and restaurant suggestions. It can even simulate social scenarios, such as acting as a hiring manager to help a user practice their answers for an upcoming job interview.
Access, Versions, And Modalities

OpenAI offers different ways to interact with the technology depending on user needs and budget. While the core experience remains text-based, recent updates have expanded the sensory capabilities of the model, allowing it to interact with the world more like a human does.
Free vs. Paid Tiers
The standard version of ChatGPT is generally free to use. This tier provides access to a capable model that handles most daily tasks effectively, though users may experience slower response times during peak hours.
The paid subscription, often called ChatGPT Plus, unlocks more powerful models. These advanced versions offer faster generation speeds, higher accuracy in reasoning, and priority access when the network is busy.
Paid users often get early access to new features before they roll out to the general public.
Multimodal Capabilities
Modern iterations of the software are “multimodal,” meaning they can process more than just text.
- Vision: Users can upload photographs, charts, or screenshots. The AI can describe the image, analyze data in a graph, or help troubleshoot a broken appliance if shown a picture of the part.
- Voice: The mobile app supports real-time voice conversations. Users can speak to the AI and hear a spoken response, making it useful for language practice or hands-free queries.
- Generation: Through integration with image-generation models like DALL-E, ChatGPT can create original images based on descriptive text prompts.
Platform Availability
Accessibility is broad across different devices. The primary access point is through a web browser on any computer.
For mobile use, dedicated applications exist for both iOS and Android, which is where voice features are most commonly used. There are also desktop applications for macOS and Windows, allowing deeper integration into a user’s computer workflow.
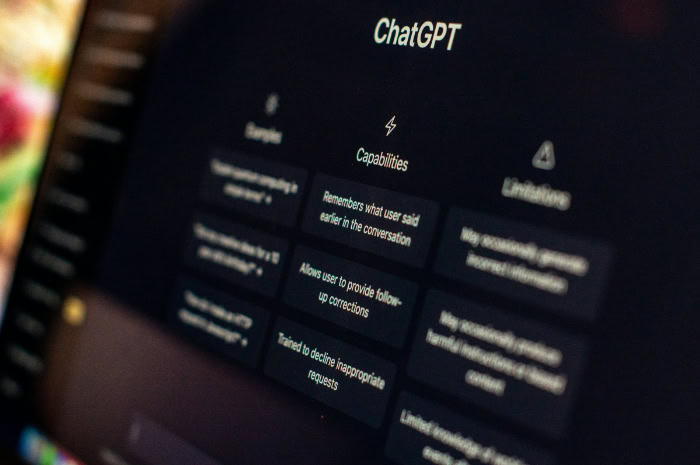
Critical Limitations And Risks

Despite its capabilities, ChatGPT allows for significant errors and misuse. It is not a truth engine, and treating it as an infallible source of information can lead to embarrassing or dangerous mistakes.
Users must maintain a skeptical mindset and verify outputs, particularly when dealing with factual or sensitive topics.
The “Hallucination” Problem
The most persistent issue with Large Language Models is their tendency to “hallucinate.” This occurs when the AI confidently generates false information.
Because the model prioritizes linguistic flow and pattern matching over factual accuracy, it may invent dates, legal cases, historical events, or scientific facts that sound plausible but are entirely incorrect. The AI rarely admits it does not know the answer; it simply invents one.
Contextual Memory Limits
While the AI can recall details from earlier in a conversation, its memory is not infinite. Every model has a “context window,” which is a limit on how much text it can process at once.
If a conversation drags on for too long or involves too many large documents, the model will “forget” the beginning of the chat. This can lead to circular arguments or the loss of specific instructions provided earlier in the session.
Data Privacy And Security
Users should assume that conversations are not private by default. OpenAI typically retains the right to review chats to improve their systems, and in some configurations, conversation data helps train future models.
This poses a risk for employees who paste confidential business data, proprietary code, or sensitive customer information into the chat. Anything shared with the chatbot could potentially become part of the collective knowledge base or be viewed by human reviewers during safety checks.
Bias And Safety Filters
The model reflects the biases found in the internet data it consumed during training. This means it can occasionally produce output that reinforces stereotypes or provides slanted viewpoints on political or social issues.
To combat this, developers have installed safety filters and guardrails. These mechanisms attempt to block hate speech, instructions for illegal acts, and other harmful content, but they are not perfect.
The model may sometimes be overly cautious, refusing to answer harmless questions, or conversely, it may fail to catch subtle forms of bias.
Conclusion
ChatGPT represents a significant shift in how we handle information and creative work. It functions best as a tireless assistant or a brainstorming partner rather than a substitute for human competence.
The software excels at heavy lifting such as organizing data, drafting structures, and generating options, but it lacks the nuance, intent, and accountability that a person brings to the table. It serves as a powerful engine for productivity, yet it requires a driver to steer it correctly.
This dynamic necessitates a “human in the loop” approach. The output generated by the AI should serve as a starting point, not the final product.
Relying blindly on its answers invites error, so the user must act as an editor and fact-checker. Critical thinking remains essential; verifying dates, logic, and sources is the responsibility of the person behind the keyboard.
The text the model produces is only as safe and accurate as the oversight applied to it.
As the technology advances, the way we interact with it will continue to change. Mastery of these tools is not about memorizing a set of commands but about developing the judgment to apply them effectively.
Treating ChatGPT as a dynamic utility rather than a magic solution allows users to harness its speed without sacrificing quality. Staying curious and adaptable is the best strategy for remaining effective as these systems grow more capable.

