What Is ISP Throttling? Causes and Signs You Should Know

Your internet connection might not always be as fast as it seems, even when you're paying for top-tier speeds. This frustrating slowdown could be the result of ISP throttling—a practice where internet service providers intentionally limit your connection speed.
Whether it’s streaming your favorite show, downloading large files, or enjoying an online game, throttling can disrupt these activities and leave you wondering why your connection isn’t performing as promised.
Far from rare, throttling is a common occurrence that many users experience without even realizing it. ISPs often cite network management or data caps as reasons for slowing connections, but the line between reasonable management and unfair practices can be blurry.
How ISP Throttling Works
Internet users often notice sudden drops in speed or performance, especially when engaging in high-bandwidth activities like streaming or online gaming. While these slowdowns may appear random, they are sometimes the result of intentional actions by internet service providers (ISPs) to control network traffic.
This deliberate reduction in speed is known as ISP throttling. To understand its impact, it’s essential to grasp how throttling is carried out and the forms it can take.
Basic Mechanics
ISP throttling relies on sophisticated technology to manage and limit the data flow of certain users or activities. The goal is to alleviate pressure on the network or adhere to specific policies, often at the expense of the user’s experience.
One of the primary techniques used in throttling is bandwidth limitation. ISPs can set upper limits on the data speed for certain users or applications, ensuring that bandwidth is distributed to other parts of the network.
For instance, if one user is streaming a high-definition video, the ISP may slow their connection to prevent overloading the system during peak usage.
Another tool ISPs rely on is deep packet inspection (DPI). DPI allows them to analyze specific packets of data traveling through the network.
By examining these packets, ISPs can identify the type of activity—such as video streaming or torrenting—and apply throttling selectively based on their findings. While DPI is often justified for legitimate purposes like security or network management, it is also used to enforce throttling policies.
Traffic monitoring is another critical aspect of throttling. ISPs keep a close watch on network usage patterns to detect behaviors or activities that might strain the system.
By analyzing trends in data consumption, they can identify opportunities to throttle certain connections or activities without affecting the broader network.
Types of Throttling
Throttling is not a one-size-fits-all practice. ISPs use multiple approaches, each tailored to specific goals or constraints.
These practices can vary widely, affecting different activities, times of day, or levels of data usage.
One common form is application-specific throttling. In this case, ISPs target specific applications or services, such as streaming platforms like Netflix or YouTube.
By slowing down data speeds for these services, ISPs can manage the load on their networks while potentially steering users toward alternative content providers—sometimes even their own.
Another approach is time-based throttling. During peak usage hours, when many users are online simultaneously, ISPs may introduce temporary speed limits to prevent the network from becoming overwhelmed.
This ensures that users with less intense data requirements can still enjoy a stable connection.
Data cap enforcement represents yet another method. Many ISP plans include monthly data limits, and users exceeding these caps may find their speeds severely reduced.
This practice is particularly common with mobile networks and serves as both a cost control mechanism and a disincentive for heavy data usage.
Each of these methods reflects the varied ways ISPs aim to balance their operational goals with user needs, although the fairness of such practices often sparks debate.
Common Triggers

ISP throttling isn’t random; certain activities and scenarios tend to activate these intentional slowdowns. These triggers often revolve around high-bandwidth usage or situations that challenge the stability of a network.
Recognizing when throttling is most likely to occur can help users identify its presence and take steps to mitigate its effects.
High-Bandwidth Activities
Certain online activities place a significant demand on an ISP’s infrastructure, prompting them to throttle connections to balance resources. Streaming services, for instance, require substantial amounts of data to deliver high-quality video content.
When users watch movies or shows in high definition or 4K, the strain on the network grows even more pronounced. To manage this, ISPs often reduce streaming speeds, leading to buffering or a noticeable drop in playback quality.
Online gaming is another common trigger. Modern games demand low latency and high-speed connections to provide a seamless experience.
However, when large numbers of gamers connect during popular times, the resulting data traffic can impact network performance. ISPs may respond by throttling gaming-related traffic, leading to increased lag or slower performance, which can frustrate players.
Large file downloads, including software updates or multimedia content, also consume significant bandwidth. When users repeatedly download massive files, ISPs might perceive their activity as excessive and throttle their speeds.
This practice helps preserve overall network stability but often leaves users waiting longer than expected for their downloads to complete.
Network Management
In addition to high-bandwidth activities, ISPs rely on throttling as a tool for managing their networks during challenging conditions. For example, peak usage hours, such as evenings when people are home streaming, gaming, or communicating online, often push networks to their capacity.
To prevent widespread slowdowns or outages, ISPs may reduce speeds for some users during these hours.
Network congestion can also occur unexpectedly, such as during major events or when multiple users in a specific area are online simultaneously. In these cases, ISPs use throttling to redistribute bandwidth and ensure that at least a basic level of service remains available for everyone.
Fair usage policies also play a significant role in triggering throttling. Many ISPs implement these policies to prevent excessive data usage from a small group of users, which they argue could impact others on the network.
If a user’s activity exceeds the acceptable threshold outlined in their plan, throttling is often employed to curtail their speeds for the remainder of the billing cycle or specific period.
Detection Methods
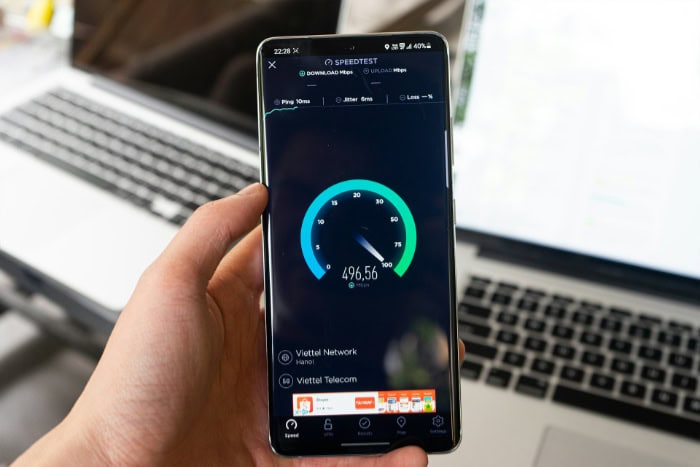
Determining whether your internet connection is being throttled can feel challenging, especially since ISPs rarely inform users outright. However, with careful observation and some basic tools, it is possible to spot the signs of throttling.
This involves monitoring overall performance and paying close attention to how specific activities behave online.
Performance Monitoring
One of the most effective ways to detect throttling is through performance monitoring. Regularly testing your internet speed can provide significant insights.
By running speed tests at various times of the day and comparing the results, you may notice patterns. For instance, speeds might drop during peak hours or remain consistently lower than what you were promised in your service agreement.
Pattern recognition plays a crucial role in detecting throttling. If you find that speed reductions occur only during specific activities, such as streaming videos or gaming online, it is often a clear sign that ISPs are selectively slowing down those types of traffic.
Recognizing repeated disruptions tied to particular behaviors can help confirm the presence of throttling.
Traffic analysis tools also prove useful in identifying throttling. Certain tools are designed to analyze your internet traffic and compare it against standard benchmarks, helping to detect irregularities.
These tools can also identify changes in how data is being routed or prioritized, offering a deeper look into potential ISP interference.
Service-Specific Signs
Sometimes, the effects of throttling are more apparent during specific activities rather than general usage. Streaming quality, for example, is often an early indicator.
If you’re watching content on platforms like YouTube or Netflix and suddenly experience buffering or a noticeable drop in resolution, throttling could be the reason. This is especially likely if your connection otherwise performs well during non-streaming tasks.
Latency issues during online gaming also raise red flags. Smooth gameplay relies on a stable, fast connection.
If your game starts lagging or disconnecting frequently, especially during times of peak activity, your ISP may be slowing gaming traffic to manage their network.
Similarly, fluctuations in download speeds can signal throttling. When downloading files or software updates, you might notice that the process is slower than usual—even if other online activities seem unaffected.
This selective reduction in download speeds is often tied to ISPs targeting bandwidth-heavy tasks.
Legal Framework

The legal landscape surrounding ISP throttling reflects an ongoing balance between the rights of consumers and the operational needs of internet service providers. Regulations vary by region, influencing how ISPs are allowed to manage their networks and informing users of their rights.
Additionally, service agreements often set the terms for what users can expect, underscoring the importance of reviewing the policies tied to their internet plans.
Regulatory Environment
Net neutrality has long been a cornerstone of debates surrounding throttling. Net neutrality principles demand that ISPs treat all internet traffic equally, prohibiting them from favoring or throttling specific websites, platforms, or applications.
In regions where net neutrality protections are strong, such as the European Union, throttling practices are more tightly regulated. However, in countries where net neutrality rules have been weakened or repealed, ISPs may have greater freedom to implement throttling without legal repercussions.
ISP disclosure requirements also play a crucial role in regulating throttling practices. Some governments require ISPs to transparently disclose if, when, and why they throttle connections.
These notices are often buried in terms and conditions, but they are an important mechanism for ensuring some level of accountability. Transparency allows users to know when their connection may be intentionally slowed and under what circumstances.
Consumer rights regarding throttling are intertwined with both transparency and broader regulatory frameworks. In regions with robust consumer protection laws, users may be able to challenge throttling practices that are deemed unfair or misleading.
For instance, if an ISP advertises unlimited high-speed data but throttles users after a certain threshold, customers may have grounds to file complaints or seek refunds.
Service Agreements
Service agreements between ISPs and customers often define the boundaries of throttling practices, though many users may overlook the details hidden in these agreements. Fair use policies, for example, frequently appear in contracts for broadband and mobile plans.
These policies outline acceptable levels of usage and may permit ISPs to throttle connections for users who exceed the stated limits. While framed as a way to ensure equal access for all customers, these policies sometimes clash with user expectations, particularly for those on “unlimited” plans.
Data cap terms are another common feature of service agreements that can directly lead to throttling. Many ISPs set monthly data limits for their plans and reserve the right to throttle speeds once these caps are reached.
Such practices are often justified as a means of managing costs and preventing excessive use. However, customers should carefully examine these limits, especially when selecting plans intended for high-bandwidth activities like streaming or gaming.
Speed guarantees, or the lack thereof, are also worth noting. Many ISPs advertise speeds as “up to” a certain level, which leaves room for variation and throttling.
Customers expecting consistent speeds may feel misled when their performance dips significantly, particularly during throttling events. While ISPs often include disclaimers about speed variability in their agreements, clear-cut guarantees are rare, giving them considerable flexibility in managing network performance.
Mitigation Strategies
For users experiencing ISP throttling, there are ways to reduce its impact and regain better control over their connection. These strategies range from technical tools that obscure your activity to simple changes in how and when you use your internet.
While no solution is one-size-fits-all, combining multiple approaches can significantly improve your experience and lessen the frustrations caused by throttling.
Technical Solutions
One of the most effective methods to counter throttling is using a VPN (Virtual Private Network). A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through one of its servers, effectively masking your online activities from your ISP.
Since ISPs often rely on deep packet inspection to identify specific types of traffic for throttling, a VPN can make it far harder for them to differentiate streaming, gaming, or file downloads from regular browsing. This additional layer of privacy not only helps bypass throttling but also enhances overall security.
Another approach involves modifying your DNS settings. ISPs often use their own DNS servers to monitor and control internet traffic.
Switching to a third-party DNS provider, such as Google Public DNS or Cloudflare, can sometimes reduce throttling, particularly in cases where ISPs prioritize or redirect traffic through their infrastructure. Changing your DNS settings is a simple process that can speed up certain connections and improve overall performance.
Traffic encryption also plays a critical role in bypassing throttling. Whether through a VPN or other encryption tools, disguising the specific details of your internet activity makes it harder for ISPs to selectively throttle content.
Many websites and applications already use HTTPS encryption, but additional layers can further protect sensitive activities like gaming or streaming and prevent targeted slowdowns.
Consumer Actions
Beyond technical solutions, adjusting how you use your internet can also help mitigate throttling. Optimizing your ISP plan to better align with your needs is an important first step.
For example, if you frequently run into data caps or experience slowdowns due to fair use limits, upgrading to a higher-tier plan could offer more flexibility. Alternatively, switching to a plan that explicitly includes unlimited high-speed data might alleviate throttling triggered by exceeding usage thresholds.
Timing your online activities to avoid peak hours can also make a noticeable difference. Since ISPs often throttle connections to manage congestion during busy periods, using bandwidth-heavy services like streaming or gaming at less popular times may provide faster speeds.
While not a perfect solution, this approach can help you work around the network's busiest moments and minimize disruptions.
If throttling becomes a persistent issue despite other efforts, exploring alternative service providers is worth considering. Some ISPs are more transparent about their throttling policies and offer better terms, such as higher data caps or stricter adherence to net neutrality principles.
Researching competing providers in your area and comparing their offerings may reveal better options that align with your usage habits and expectations.
Conclusion
ISP throttling remains a pressing concern for many internet users, impacting everything from streaming quality to gaming performance. By gaining insight into how throttling works, recognizing its triggers, and learning how to detect it, users are better equipped to address the issue when it arises.
While the legal and regulatory framework surrounding throttling continues to evolve, service agreements and ISP policies often dictate the extent to which throttling is applied.
Fortunately, there are practical strategies available to minimize its effects. From leveraging technical tools like VPNs and DNS modifications to making smarter choices regarding ISP plans and usage patterns, there are ways to regain control over your internet experience.
Staying informed about your rights as a consumer and being proactive about your connectivity needs can make a world of difference. The internet should be a space of seamless access and freedom, and knowing how to navigate throttling helps ensure it stays that way.


